Nursing care complex oxygenation alterations – Nursing care for complex oxygenation alterations is a multifaceted and essential aspect of patient care, encompassing a wide range of interventions and considerations. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the topic, exploring respiratory assessment, oxygen therapy, pharmacological management, nursing interventions, patient education, and case study analysis.
Understanding the complexities of complex oxygenation alterations and the appropriate nursing interventions is crucial for improving patient outcomes and ensuring optimal respiratory function.
Respiratory Assessment
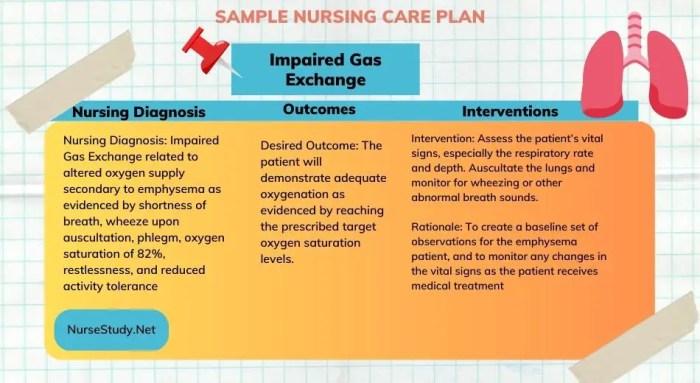
Assessing respiratory function is crucial in patients with complex oxygenation alterations. It helps identify the underlying cause, monitor disease progression, and guide treatment decisions.
Techniques used for respiratory assessment include:
- Pulse oximetry:Measures oxygen saturation in the blood.
- Arterial blood gas analysis:Determines pH, partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2), partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2), and bicarbonate levels.
- Chest X-ray:Visualizes the lungs and airways, revealing abnormalities such as pneumonia, lung edema, or atelectasis.
Abnormal respiratory findings may include:
- Hypoxemia:Low blood oxygen levels (PaO2< 60 mmHg).
- Hypercapnia:Elevated blood carbon dioxide levels (PaCO2 > 45 mmHg).
- Respiratory acidosis:Decreased blood pH due to CO2 retention.
- Respiratory alkalosis:Increased blood pH due to hyperventilation.
Oxygen Therapy

Oxygen therapy is a mainstay in managing complex oxygenation alterations. It involves delivering supplemental oxygen to the patient to improve tissue oxygenation.
Types of oxygen therapy include:
- Nasal cannula:Delivers oxygen through small tubes inserted into the nostrils.
- Face mask:Covers the nose and mouth, providing a higher oxygen concentration.
- Mechanical ventilation:Uses a ventilator to deliver oxygen and support breathing in critically ill patients.
Oxygen therapy improves oxygenation by:
- Increasing the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli.
- Improving diffusion of oxygen across the alveolar-capillary membrane.
- Reducing the work of breathing.
Potential complications of oxygen therapy include:
- Oxygen toxicity:Can damage the lungs if used at high concentrations for prolonged periods.
- Nasal irritation:Nasal cannulas can cause dryness and discomfort.
- Barotrauma:Mechanical ventilation can cause lung injury if not used properly.
Pharmacological Management
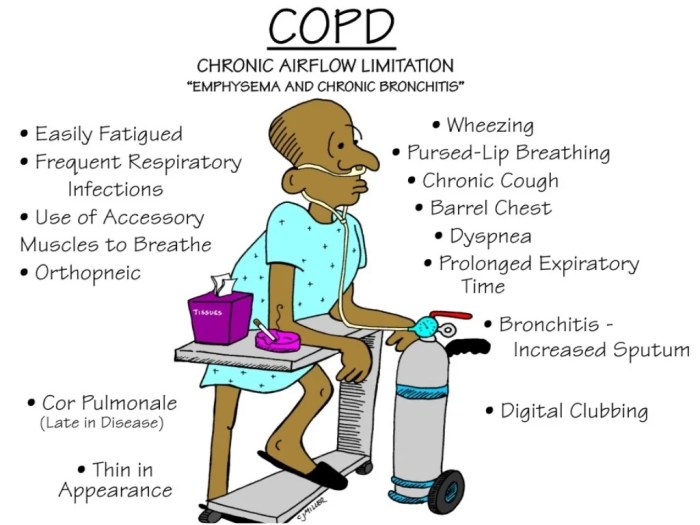
Medications play a crucial role in treating complex oxygenation alterations by improving respiratory function and reducing inflammation.
Classes of medications used include:
- Bronchodilators:Relax airway smooth muscles, improving airflow.
- Corticosteroids:Reduce inflammation in the airways.
- Antibiotics:Treat infections that contribute to respiratory distress.
Mechanisms of action of these medications include:
- Bronchodilators:Bind to beta-2 receptors, causing relaxation of airway smooth muscles.
- Corticosteroids:Bind to glucocorticoid receptors, reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune response.
- Antibiotics:Target specific bacteria or viruses, killing or inhibiting their growth.
Potential side effects of these medications include:
- Bronchodilators:Tachycardia, tremors, nervousness.
- Corticosteroids:Fluid retention, weight gain, immunosuppression.
- Antibiotics:Gastrointestinal upset, allergic reactions, antibiotic resistance.
FAQ Insights: Nursing Care Complex Oxygenation Alterations
What is the primary goal of nursing care for complex oxygenation alterations?
The primary goal is to maintain adequate oxygenation and prevent further complications.
What are some common signs and symptoms of complex oxygenation alterations?
Shortness of breath, rapid breathing, wheezing, and cyanosis.
What are the different types of oxygen therapy that may be used?
Nasal cannula, face mask, and mechanical ventilation.