Investigating the Earth’s crustal plates by studying earthquakes and volcanoes offers a profound understanding of our planet’s dynamic processes. Earthquakes, the result of sudden energy releases along faults, and volcanoes, the conduits of molten rock from the Earth’s interior, provide invaluable insights into the structure and behavior of these plates.
The study of these phenomena not only unveils the intricacies of plate tectonics but also holds immense practical significance, enabling us to mitigate natural disasters, develop innovative technologies, and glimpse into the future of our ever-changing planet.
Earth’s Crustal Plates
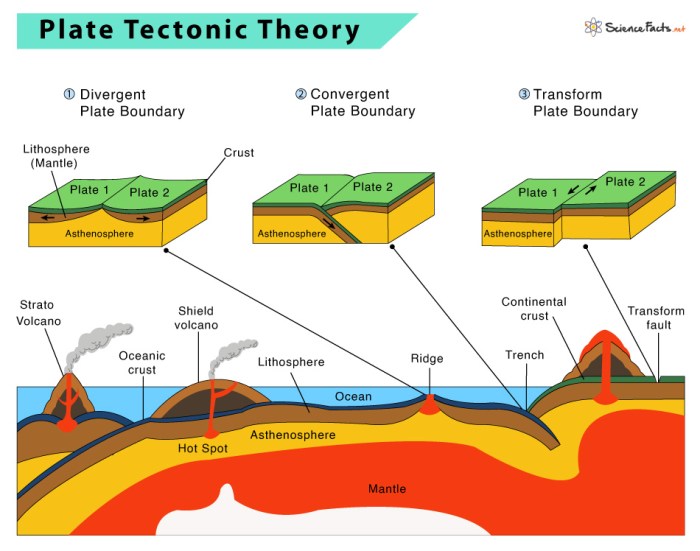
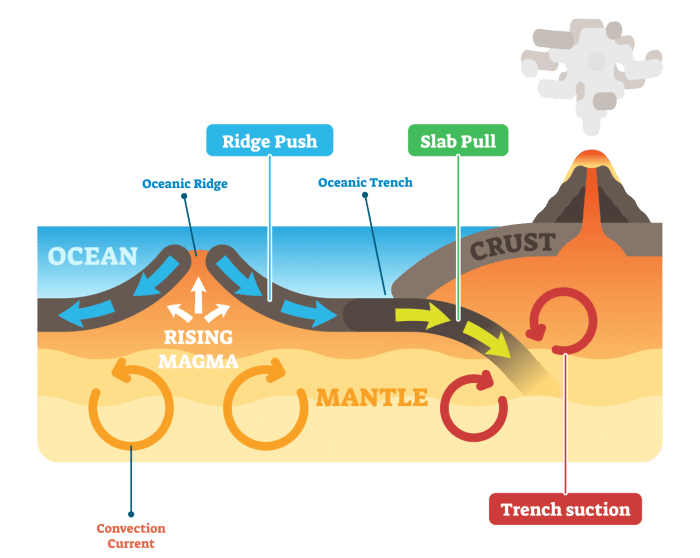
The Earth’s crust is divided into several large, rigid plates that float on the Earth’s mantle. These plates are in constant motion, moving past each other at their boundaries. The theory of plate tectonics describes the movement of these plates and the geological phenomena that occur at their boundaries.
The Earth’s crustal plates are made up of two types of material: continental crust and oceanic crust. Continental crust is thicker and less dense than oceanic crust, and it forms the continents. Oceanic crust is thinner and denser than continental crust, and it forms the ocean floor.
Types of Crustal Plates
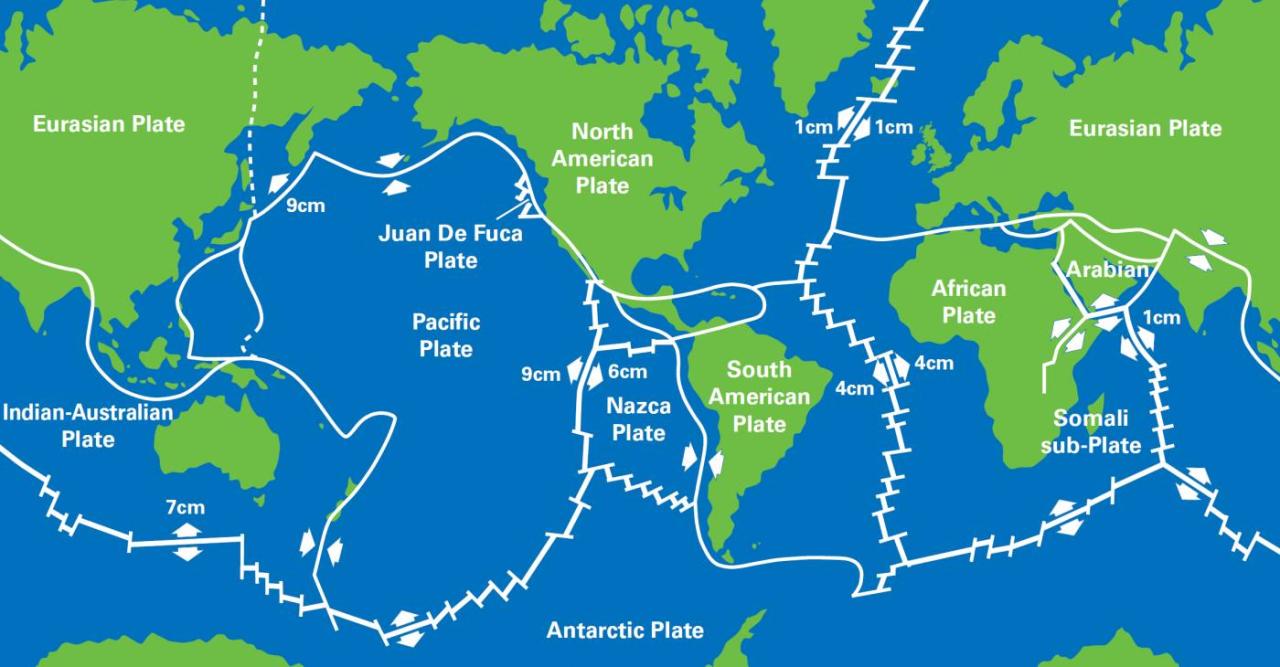
- Continental plates: These plates are made up of continental crust and are the largest and thickest plates. They include the North American Plate, the South American Plate, the Eurasian Plate, the African Plate, the Australian Plate, and the Antarctic Plate.
- Oceanic plates: These plates are made up of oceanic crust and are thinner and denser than continental plates. They include the Pacific Plate, the Atlantic Plate, and the Indian Plate.
Earthquakes
Earthquakes are vibrations of the Earth’s surface that are caused by the sudden release of energy below the Earth’s surface. Earthquakes can range in intensity from barely perceptible to violent, and they can cause widespread damage and loss of life.
Causes of Earthquakes
Earthquakes are caused by the movement of the Earth’s crustal plates. When two plates collide, one plate may be forced to move beneath the other. This process, called subduction, can cause the rocks in the subducting plate to melt and rise to the surface, forming volcanoes.
If the subducting plate is not completely melted, it can build up pressure and eventually cause an earthquake.
Earthquakes can also be caused by the movement of faults. Faults are fractures in the Earth’s crust where rocks have broken. When rocks on either side of a fault move past each other, an earthquake can occur.
Types of Earthquakes, Investigating the earth’s crustal plates by studying earthquakes and volcanoes
- Tectonic earthquakes: These earthquakes are caused by the movement of the Earth’s crustal plates. They are the most common type of earthquake.
- Volcanic earthquakes: These earthquakes are caused by the movement of magma or other volcanic fluids. They are often associated with volcanic eruptions.
- Collapse earthquakes: These earthquakes are caused by the collapse of underground caves or other structures. They are relatively rare.
Volcanoes: Investigating The Earth’s Crustal Plates By Studying Earthquakes And Volcanoes
Volcanoes are mountains that form when magma, or molten rock, rises to the surface of the Earth and erupts. Volcanoes can be active, dormant, or extinct.
Causes of Volcanic Eruptions
Volcanic eruptions are caused by the movement of the Earth’s crustal plates. When two plates collide, one plate may be forced to move beneath the other. This process, called subduction, can cause the rocks in the subducting plate to melt and rise to the surface.
If the magma reaches the surface, it can erupt from a volcano.
Types of Volcanic Eruptions
- Effusive eruptions: These eruptions are characterized by the flow of lava from a volcano. Lava is molten rock that has a low viscosity, which means that it can flow easily.
- Explosive eruptions: These eruptions are characterized by the ejection of ash and other volcanic material from a volcano. Ash is fine-grained volcanic rock that has a high viscosity, which means that it cannot flow easily.
Studying Earthquakes and Volcanoes

Earthquakes and volcanoes are two of the most powerful forces on Earth. They can cause widespread damage and loss of life, but they can also provide valuable information about the Earth’s interior.
Scientists study earthquakes and volcanoes using a variety of methods. These methods include:
- Seismology: Seismology is the study of earthquakes. Seismologists use seismometers to record the ground motion caused by earthquakes. This data can be used to determine the location, magnitude, and depth of an earthquake.
- Volcanology: Volcanology is the study of volcanoes. Volcanologists use a variety of methods to study volcanoes, including observing volcanic eruptions, measuring volcanic gases, and collecting volcanic samples.
The study of earthquakes and volcanoes is important for several reasons. First, it can help us to understand the Earth’s interior and how it works. Second, it can help us to develop early warning systems for earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Third, it can help us to mitigate the damage caused by earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the different types of crustal plates?
Crustal plates are classified into two main types: oceanic plates, composed primarily of dense oceanic crust, and continental plates, which are thicker and less dense, carrying continents and their associated features.
How do earthquakes help us study crustal plates?
Earthquakes generate seismic waves that travel through the Earth’s layers, providing valuable information about the structure and composition of crustal plates. By analyzing these waves, scientists can determine the thickness, density, and other properties of the plates.
What role do volcanoes play in understanding plate tectonics?
Volcanic eruptions release magma from the Earth’s mantle, providing direct access to materials from deep within the planet. Studying volcanic rocks and gases helps scientists understand the composition and dynamics of the Earth’s interior, including the processes that drive plate tectonics.