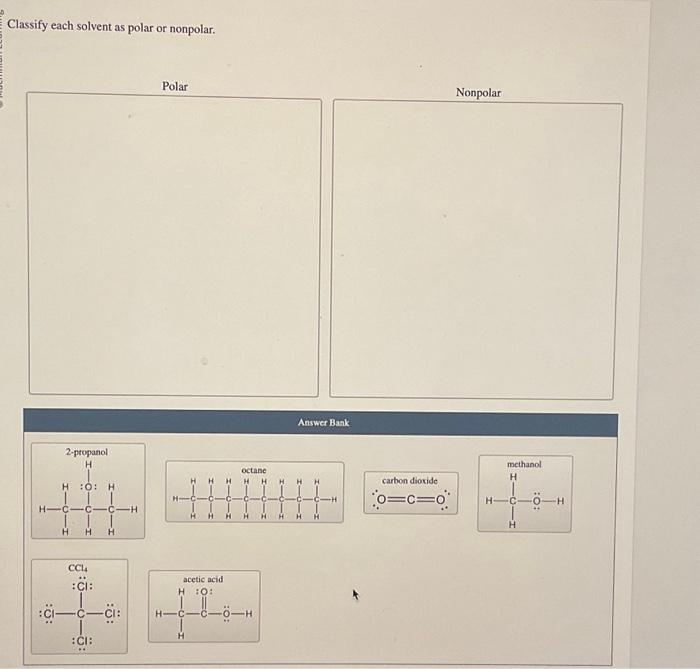
Classify each solvent as polar or nonpolar – In chemistry, the polarity of solvents plays a crucial role in various applications. This guide explores the concept of solvent polarity, provides examples, and discusses its significance in solvent selection and interactions. Understanding solvent polarity enables chemists to optimize processes and achieve desired outcomes.
Polar solvents, characterized by an uneven distribution of charge, readily dissolve ionic compounds and polar solutes. Nonpolar solvents, on the other hand, have a symmetrical charge distribution and are suitable for dissolving nonpolar solutes. The polarity of a solvent influences its interactions with solutes, affecting solubility, reaction rates, and other chemical processes.
Solvent Properties

Solvents are substances that can dissolve other substances. They are classified as either polar or nonpolar based on their molecular structure and the distribution of their electrons.
Polar solvents have a net positive or negative charge, while nonpolar solvents have no net charge. The polarity of a solvent is determined by the electronegativity of its atoms. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself.
Polar solvents are good at dissolving polar solutes, while nonpolar solvents are good at dissolving nonpolar solutes. This is because polar solvents can form strong electrostatic interactions with polar solutes, while nonpolar solvents cannot.
Examples of Polar and Nonpolar Solvents, Classify each solvent as polar or nonpolar
- Polar solvents: water, methanol, ethanol, acetone
- Nonpolar solvents: hexane, benzene, toluene, dichloromethane
Solvent Classification
| Solvent Name | Chemical Formula | Polarity | Examples of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | H2O | Polar | Extraction, purification, chemical reactions |
| Methanol | CH3OH | Polar | Extraction, purification, chemical reactions |
| Ethanol | C2H5OH | Polar | Extraction, purification, chemical reactions |
| Acetone | C3H6O | Polar | Extraction, purification, chemical reactions |
| Hexane | C6H14 | Nonpolar | Extraction, purification, chemical reactions |
| Benzene | C6H6 | Nonpolar | Extraction, purification, chemical reactions |
| Toluene | C7H8 | Nonpolar | Extraction, purification, chemical reactions |
| Dichloromethane | CH2Cl2 | Nonpolar | Extraction, purification, chemical reactions |
Solvent Interactions
The polarity of a solvent influences the interactions between solvents and solutes. Polar solvents can form strong electrostatic interactions with polar solutes, while nonpolar solvents cannot.
Hydrogen bonding is a type of electrostatic interaction that occurs between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. Hydrogen bonding is a strong interaction that can have a significant impact on the properties of a solvent.
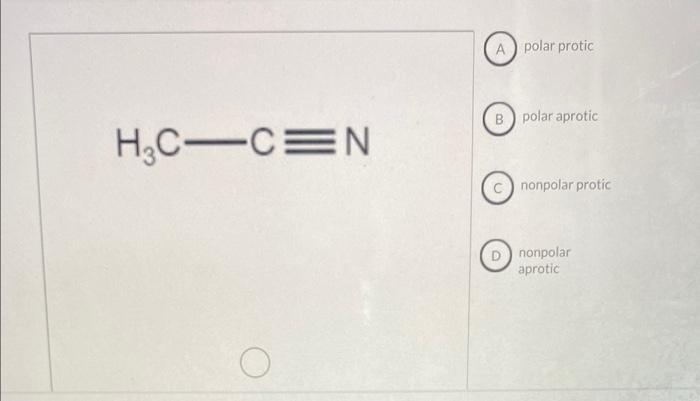
Polar solvents that can form hydrogen bonds are called protic solvents. Protic solvents are good at dissolving polar solutes that can also form hydrogen bonds. Nonpolar solvents that cannot form hydrogen bonds are called aprotic solvents. Aprotic solvents are good at dissolving nonpolar solutes that cannot form hydrogen bonds.
Solvent Applications: Classify Each Solvent As Polar Or Nonpolar
Polar and nonpolar solvents have a wide range of applications in various industries.
- Polar solvents are used in the extraction and purification of polar compounds, such as pharmaceuticals and dyes.
- Nonpolar solvents are used in the extraction and purification of nonpolar compounds, such as oils and greases.
- Polar solvents are used in chemical reactions to dissolve reactants and products.
- Nonpolar solvents are used in chemical reactions to dissolve nonpolar reactants and products.
Solvent Selection
When selecting a solvent for a specific application, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The polarity of the solvent
- The polarity of the solute
- The solubility of the solute in the solvent
- The boiling point of the solvent
- The toxicity of the solvent
The polarity of the solvent is a crucial factor in determining the suitability of a solvent for a particular task. Polar solvents are best suited for dissolving polar solutes, while nonpolar solvents are best suited for dissolving nonpolar solutes.
Answers to Common Questions
What is solvent polarity?
Solvent polarity refers to the uneven distribution of charge within a solvent molecule, resulting in a partial positive and partial negative end.
How does polarity affect solvent interactions?
Polarity influences the strength and type of interactions between solvents and solutes. Polar solvents interact strongly with polar solutes, while nonpolar solvents interact more effectively with nonpolar solutes.
Why is solvent selection important?
Choosing the appropriate solvent is crucial for optimizing chemical reactions, solubility, and other processes. Polarity is a key factor to consider when selecting a solvent for a specific application.