Hernando de soto in georgia – Hernando de Soto’s exploration of Georgia in the 16th century left an enduring mark on the state’s history and culture. His expedition brought European influence to the region, shaping interactions between Native American tribes and European settlers.
De Soto’s journey through Georgia was marked by both conflict and cultural exchange. He encountered various Native American tribes, including the Creek, Cherokee, and Apalachee, establishing alliances and engaging in battles.
Hernando de Soto’s Exploration of Georgia
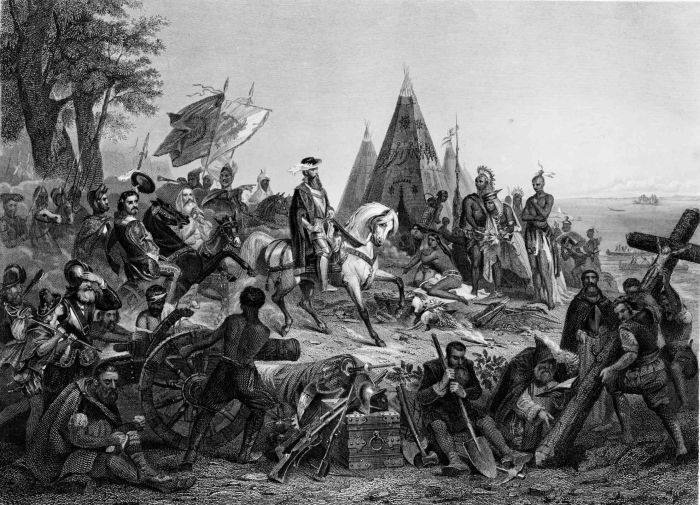

Hernando de Soto’s expedition through Georgia in the 16th century was a significant event in the history of the region. De Soto’s exploration had a profound impact on the native populations and helped shape the future of Georgia.
Route and Areas Explored
De Soto’s expedition entered Georgia from the northeast, crossing the Chattahoochee River near present-day Atlanta. He then traveled southwest through the Piedmont region, crossing the Ocmulgee and Flint Rivers. De Soto’s expedition also explored the coastal region of Georgia, including the Altamaha River and the Savannah River.
Impact on Native Populations
De Soto’s expedition had a devastating impact on the native populations of Georgia. The Spanish explorers brought diseases to which the natives had no immunity, leading to widespread death and suffering. De Soto’s men also enslaved many natives and forced them to serve as guides and porters.
The expedition’s violence and disruption caused many native communities to abandon their villages and flee into the interior.
De Soto’s Encounters with Native Americans

Hernando de Soto’s expedition through Georgia had a profound impact on both the Spanish and Native American societies. De Soto’s interactions with Native American tribes were complex and varied, ranging from peaceful cultural exchanges to violent conflicts.
Cultural Exchanges
Initially, De Soto and his men encountered Native Americans who were curious and welcoming. The Spanish were impressed by the Native Americans’ agricultural practices, their complex social structures, and their artistic skills. In turn, the Native Americans were fascinated by the Spanish horses, weapons, and armor.
Cultural exchanges occurred through trade, gift-giving, and shared meals. The Spanish introduced European goods such as metal tools, cloth, and glass beads to the Native Americans. In exchange, the Native Americans provided the Spanish with food, clothing, and information about the region.
Conflicts
However, De Soto’s expedition also led to conflicts with Native American tribes. The Spanish were often arrogant and demanding, and they often took what they wanted from the Native Americans without asking. This led to resentment and resistance.
The Spanish also carried diseases that were new to the Native Americans, such as smallpox and measles. These diseases devastated Native American populations, killing thousands of people.
Alliances
Despite the conflicts, De Soto also formed alliances with some Native American tribes. These alliances were often based on mutual respect and a common enemy. For example, De Soto allied with the Guale tribe against the Apalachee tribe.
These alliances helped De Soto to survive in a hostile environment. They also gave him access to food, supplies, and information.
Impact
De Soto’s encounters with Native Americans had a profound impact on both the Spanish and Native American societies. The Spanish gained a better understanding of the Native American cultures and the geography of the region.
However, De Soto’s expedition also had a negative impact on the Native Americans. The diseases introduced by the Spanish killed thousands of people. The conflicts between the Spanish and the Native Americans disrupted traditional ways of life and led to the loss of land and resources.
Archaeological Evidence of De Soto’s Expedition
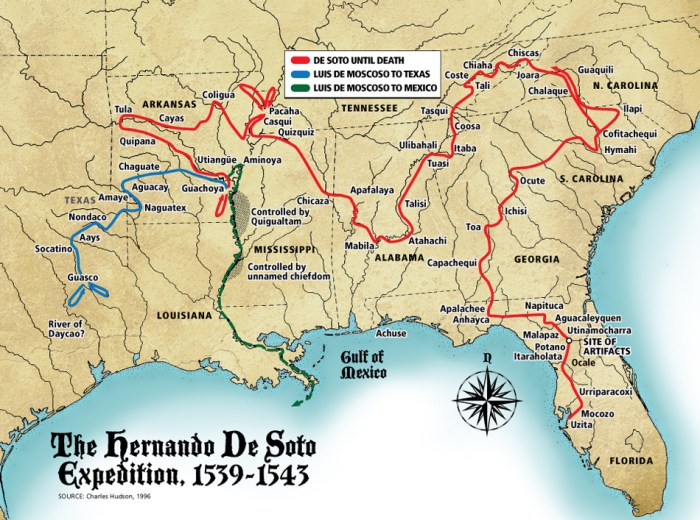
Archaeological excavations and surveys have uncovered numerous sites in Georgia associated with Hernando de Soto’s expedition. These sites provide valuable insights into the route taken by De Soto, his interactions with Native American populations, and the material culture of the expedition.
Archaeological Sites and Artifacts
The following table Artikels the key archaeological sites in Georgia linked to De Soto’s expedition:
| Site | Location | Artifacts Discovered | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Etowah Indian Mounds | Cartersville | Spanish armor, glass beads, iron tools | Evidence of a major Native American town visited by De Soto |
| Coosa | Rome | Spanish sword, crossbow bolts, Native American pottery | Site of a fierce battle between De Soto and the Coosa chiefdom |
| Mabry Mound | Athens | Spanish helmet, bronze bell, Native American arrowheads | Location of a temporary Spanish camp during the winter of 1540-41 |
| Ocmulgee Mounds | Macon | Spanish coins, musket balls, Native American tools | Evidence of De Soto’s visit to a major Mississippian culture center |
Methods of Identification and Interpretation
Archaeologists use a variety of methods to identify and interpret sites associated with De Soto’s expedition. These include:
- Historical documentation: Written accounts from Spanish chroniclers provide valuable clues about the expedition’s route and activities.
- Archaeological surveys: Surface surveys and excavations uncover artifacts and features that can be linked to the expedition.
- Geophysical techniques: Ground-penetrating radar and magnetometry can detect buried structures and artifacts.
- Comparative analysis: Artifacts found at archaeological sites are compared to known Spanish and Native American artifacts to determine their origin and significance.
By combining these methods, archaeologists have been able to piece together a detailed understanding of De Soto’s expedition and its impact on the Native American populations of Georgia.
Historical Legacy of Hernando de Soto in Georgia

Hernando de Soto’s exploration of Georgia left a lasting impact on the state’s history and development. His expedition opened up new territories for European colonization, influenced subsequent Spanish exploration and settlement efforts, and left an enduring legacy in Georgia’s culture and identity.
Influence on Spanish Colonization
De Soto’s expedition provided valuable information about the geography and resources of Georgia, which encouraged further Spanish exploration and colonization. The reports of gold and other riches found by de Soto fueled Spanish ambitions and led to the establishment of missions and settlements in the region.
De Soto’s expedition also established a precedent for Spanish exploration and conquest in the New World. His methods of exploration, including the use of force and the establishment of alliances with native tribes, became a model for subsequent Spanish expeditions in the Americas.
Enduring Legacy in Georgia’s History and Culture
De Soto’s expedition left a lasting legacy in Georgia’s history and culture. The names of many places in Georgia, such as the Chattahoochee River and the Okefenokee Swamp, are derived from Native American words recorded by de Soto’s chroniclers.
Hernando de Soto’s explorations in Georgia were a pivotal moment in the history of the region. However, if you’re looking for more information about healthcare providers in the area, you may want to check out npi number 858 area code . This resource provides valuable insights into healthcare providers and their services.
Nevertheless, returning to Hernando de Soto’s journey, his impact on Georgia’s development remains significant.
De Soto’s exploration also contributed to the development of Georgia’s frontier culture. The hardships and challenges faced by de Soto and his men during their expedition helped shape the character of the early settlers in Georgia, who faced similar challenges in establishing their own settlements.
Commemoration and Tourism
The legacy of Hernando de Soto’s expedition in Georgia is commemorated through various historical markers, monuments, and museums. These sites serve as tangible reminders of the explorer’s journey and its impact on the state’s history.
Historical Markers, Hernando de soto in georgia
Numerous historical markers dot the landscape of Georgia, marking significant locations associated with de Soto’s expedition. These markers provide brief historical accounts and serve as educational tools for visitors.
Monuments
Several monuments have been erected to honor de Soto and his expedition. These include:
- The De Soto National Memorial in Savannah, which features a bronze statue of the explorer and a museum.
- The De Soto Falls Historical Marker in Lumpkin County, which commemorates the site where de Soto and his men crossed the Chattahoochee River.
Museums
Several museums in Georgia showcase artifacts and exhibits related to de Soto’s expedition. These include:
- The Georgia History Museum in Savannah, which houses a collection of artifacts from de Soto’s expedition.
li>The Chieftains Museum in Macon, which features exhibits on the Native American cultures encountered by de Soto.
Tourism
Tourism plays a vital role in promoting the legacy of de Soto’s expedition in Georgia. Historical sites and museums attract visitors interested in the state’s history and culture. This tourism generates revenue and supports local economies.
Educational and Cultural Value
The commemorative efforts surrounding de Soto’s expedition have significant educational and cultural value. They preserve and share the history of Georgia, foster an appreciation for the state’s diverse heritage, and promote a sense of place among its residents.
Clarifying Questions
What was the significance of Hernando de Soto’s exploration of Georgia?
De Soto’s expedition brought European influence to Georgia, initiated colonization efforts, and documented interactions with Native American tribes.
How did De Soto’s expedition impact Native American populations?
De Soto’s encounters with Native Americans were marked by both conflict and cultural exchange. He established alliances and engaged in battles, affecting tribal dynamics.
What archaeological evidence remains from De Soto’s expedition in Georgia?
Archaeological sites associated with De Soto’s expedition have been identified, providing insights into his route, interactions with Native Americans, and the material culture of the period.
